Git for Professionals
Perfect Git Commit
-
File staging helps in better commits, (easier to manage, review code and adding commit messages).
-
Use
git diff <file>, to view the changes made to the not staged file.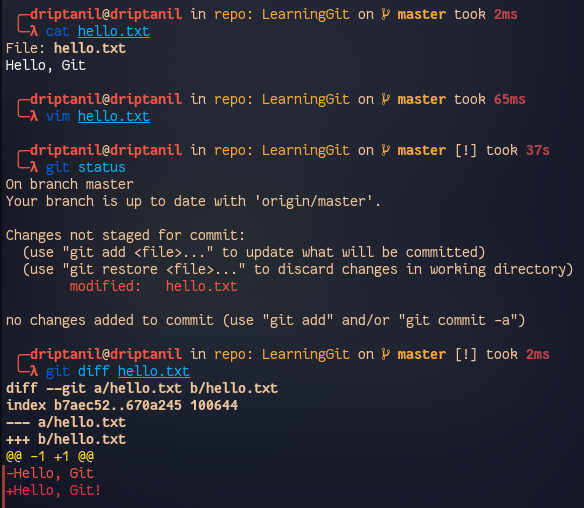
-
Use
git -pto stage certain chucks of changes in a file.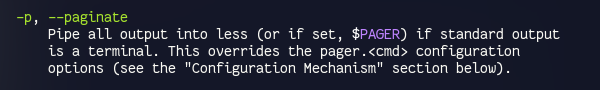
-
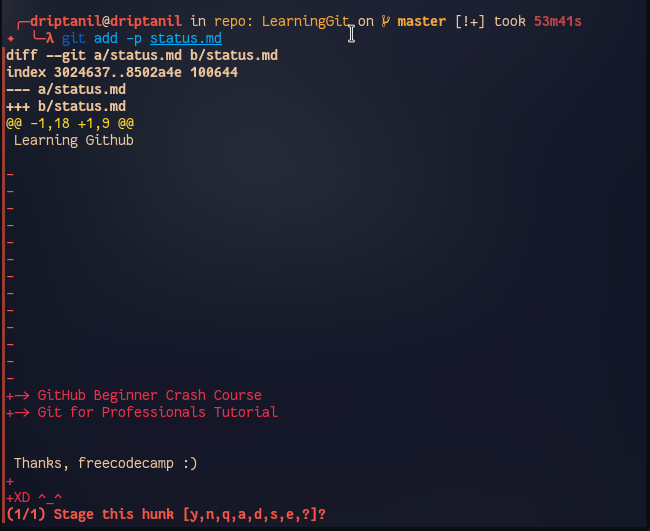
y-> stage hunkn-> do not stage hunka-> stage all remaining hunksd-> do not stage any remaining hunkss-> split the current hunke-> manually edit the current hunk
-
Use
git committo open a text editor (default: vi editor, or usegit config --global core.editor <editor_name>) -
Format for commit message:
- 1st line: Subject
- 2nd line: ``
- 3rd line: Body a. What is now different than before? b. What is the reason for the change? c. Is there anything to watch out for / anything particularly remarkable
Branching Strategies
Convention:
(agree on a Branching Work-flow in a team)
- Git allows users to create branches - learning it for better usage would improve the work-flow
- A written best practice / strategy to ideally structure work in between team members
- Team members, team size and type of project plays a huge role in managing project releases.
- Helping new on-board team members to understand the work-flow to reduce conflicts
Integrating Changes & Structuring Releases
Mainline Development
(always be integrating)
-> few branches
-> relatively small commit
-> high-quality testing & QA standards
State, Release, and Feature Branches
(Branches Enhance Structures & Workflows)
-> different types of branches
-> fulfil different types of jobs
Long-Running & Short-Lived Branches
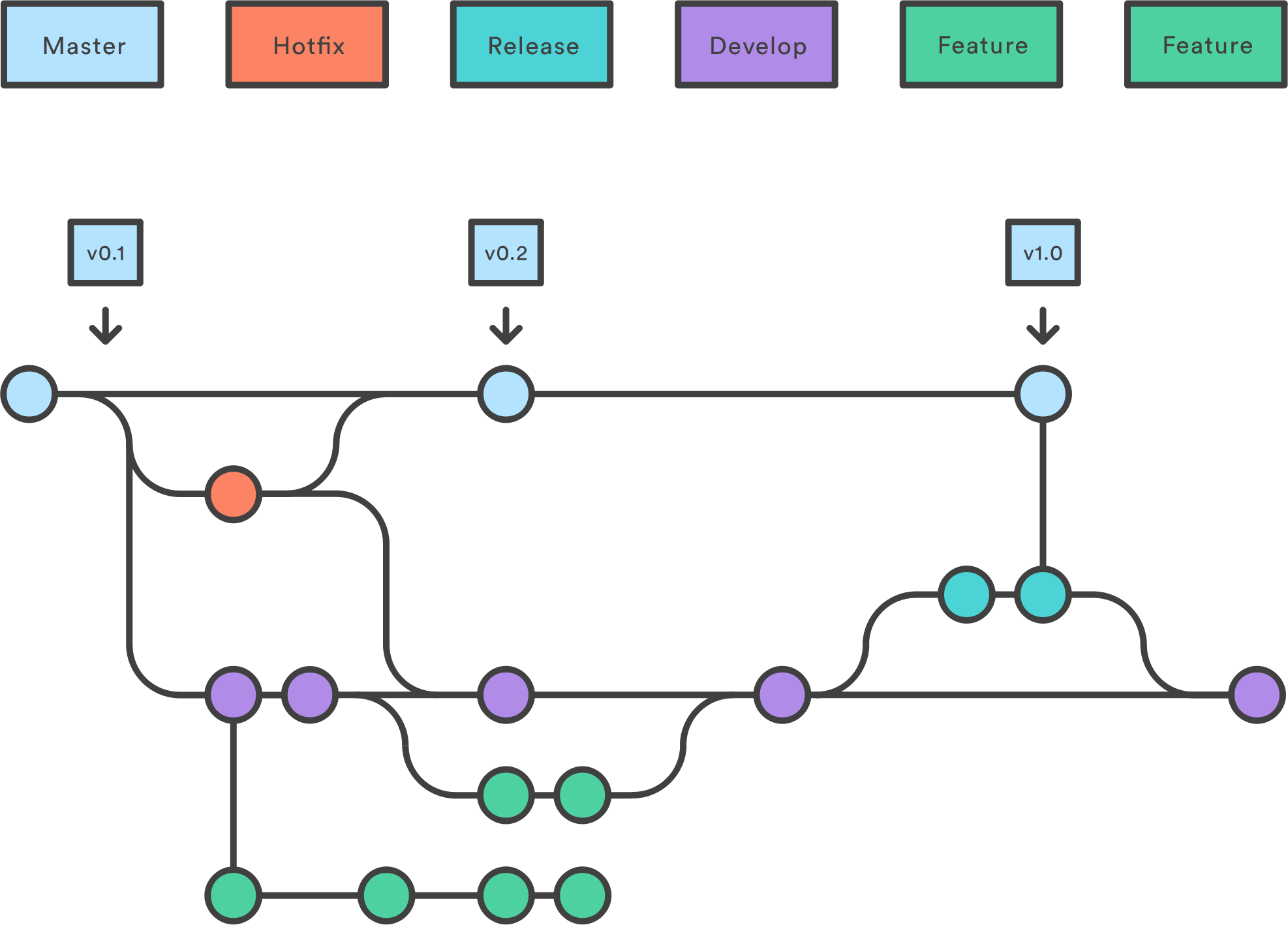
Long Running Branches
- Long Running Branches are the branches which exist through out the project.
- Every Git repository has a long running branches like main or master branch.
- Some repositories have develop or staging long running branches, generally for stability testing before merging to master branch.
- These branches represent the different stages of release and deployment.
- Commit are not directly made to long-running branches.
Short Lived Branches
- They are created for certain purposed (like new features, bug fixes, refactoring).
- They are deleted after being merged or rebased to the long running branch.
- A short lived branch is based on a long running branch.
Git Workflows
GitHub Flow
- It consists of only 1 long running branch (main) and working changes are made in short lived branches.
Git-Flow
- It consists of 2 long running branches (main + develop) and short lived branches (feature, release, hotfixes).
Develop Branch
- The develop branch serves as an integration branch of feature.
Creating develop branch
- Using git,
git branch develop&git push -u origin develop - Using git-flow extension,
git flow init
Feature Branch
- The feature branch uses develop as their parent branch and feature never directly interacts with main.
Creating feature branch
- Using git,
git checkout develop&git checkout -b feature_branch - Using git-flow extension,
git flow feature start feature_branch
Merging feature to develop
- Using git,
git checkout develop&git merge feature_branch - Using git-flow,
git flow feature finish feature_branch
Release Branch
- After develop branch has acquired enough features for a release.
- A release branch is branched off develop branch.
- Documentations, bug fixes, and release-oriented tasks of new features are pushed to release branch.
- Using git,
git checkout develop&git checkout -b release/<version>. - Using git flow extension,
git flow release start <version>. - Once release branch is ready, it is merged to main branch.
- release branch is merged back to develop branch and release branch is deleted
- Using git,
git checkout main&git merge release/<version> - Using git flow extension,
git flow release finish <version>
Hotfix Branch
- The hotfix branched off main branch, for quick patch production releases.
- As soon as the fix is complete, it is merged into main & develop branch.
- A dedicated branch for bug fixes, helps team to address issues and speed up the release cycle.
- Using git,
git checkout main&git checkout -b hotfix_branch. - Using git flow extension
git flow hotfix start hotfix_branch.
- Using git,
Pull Requests
- Pull request is request to merge changes to other repositories (pushing changes are not allowed).
- It gets many developers involved for reviewing the code and fix bugs (if any) before merging it to main branch.
Fork Repository
- Fork creates a copy of a repository with administrator permissions, to which we are allowed to make changes.





