Worker Node
A Kubernetes cluster consists of a set of worker machines, called nodes, that run containerized applications.
Each node must contain 3 node processes:
- Kubelet
- Kubeproxy
- Container Runtime
Container Runtime
- Example: Docker
Kubelet
- Kubelet is responsible for starting a pod, running a pod, assigning resources (from node to the container)
- It interacts with both container runtime and node.
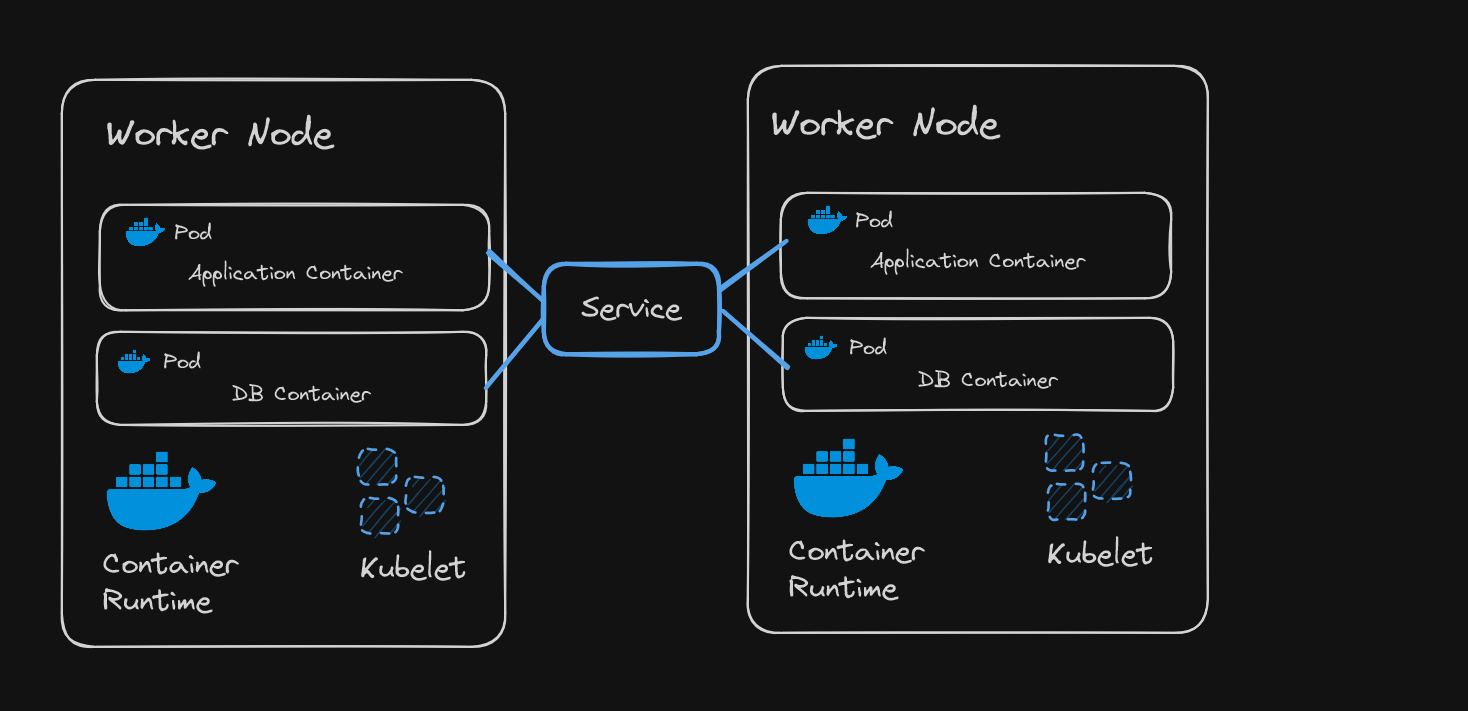
Kubernetes cluster is made of multiple nodes (replicas of one node).
Kubeproxy
- Kubeproxy responsible for forwarding requests from services to pods is actually present in same node.
- It must be assigned to every node
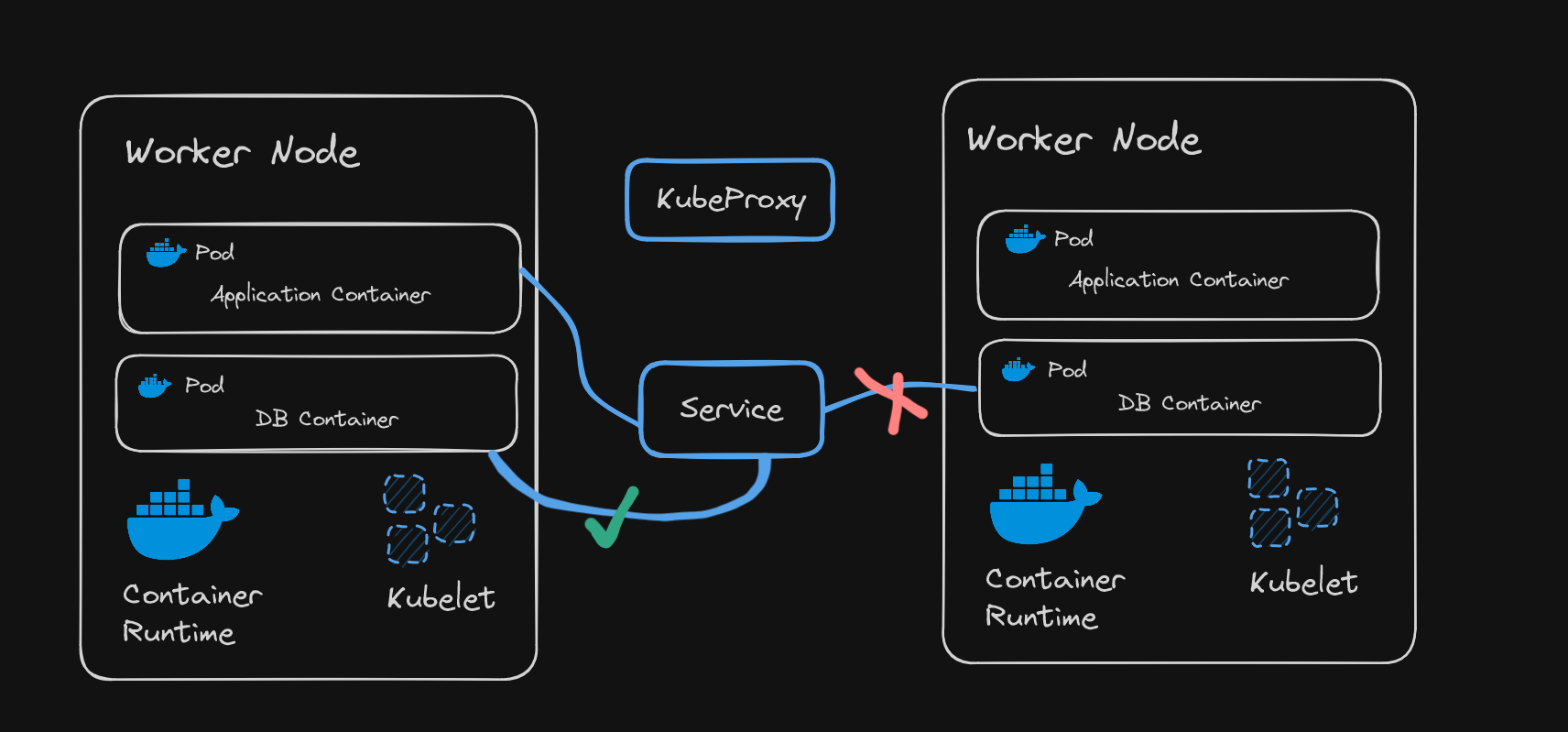
- It has intelligent forwarding logic inside in a single node, and makes sure that the performance overhead is low.
Master Node
Problem: How to interact with this cluster ?
- Schedule pod
- Monitor
- Re-schedule / Restart pod
- Join new node
Solution:
Master Node is responsible for cluster management and for providing the API that is used to configure and manage resources within the Kubernetes cluster.
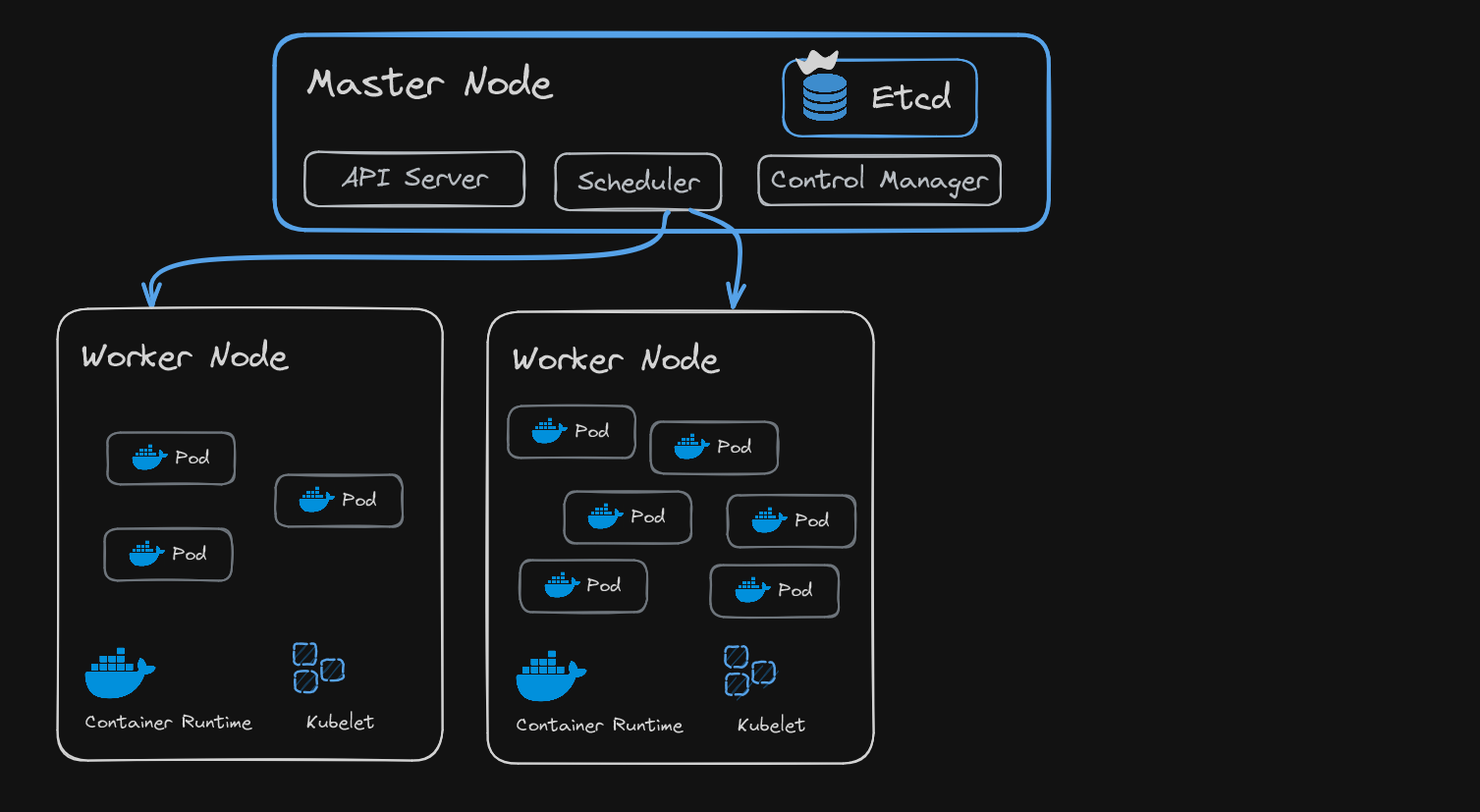
Each master node must contain 4 processes:
- API Service
- Scheduler
- Control Manager
- Etcd
API Service
- API service is a cluster gateway (entry point).
- Acts as a gatekeeper for authentication
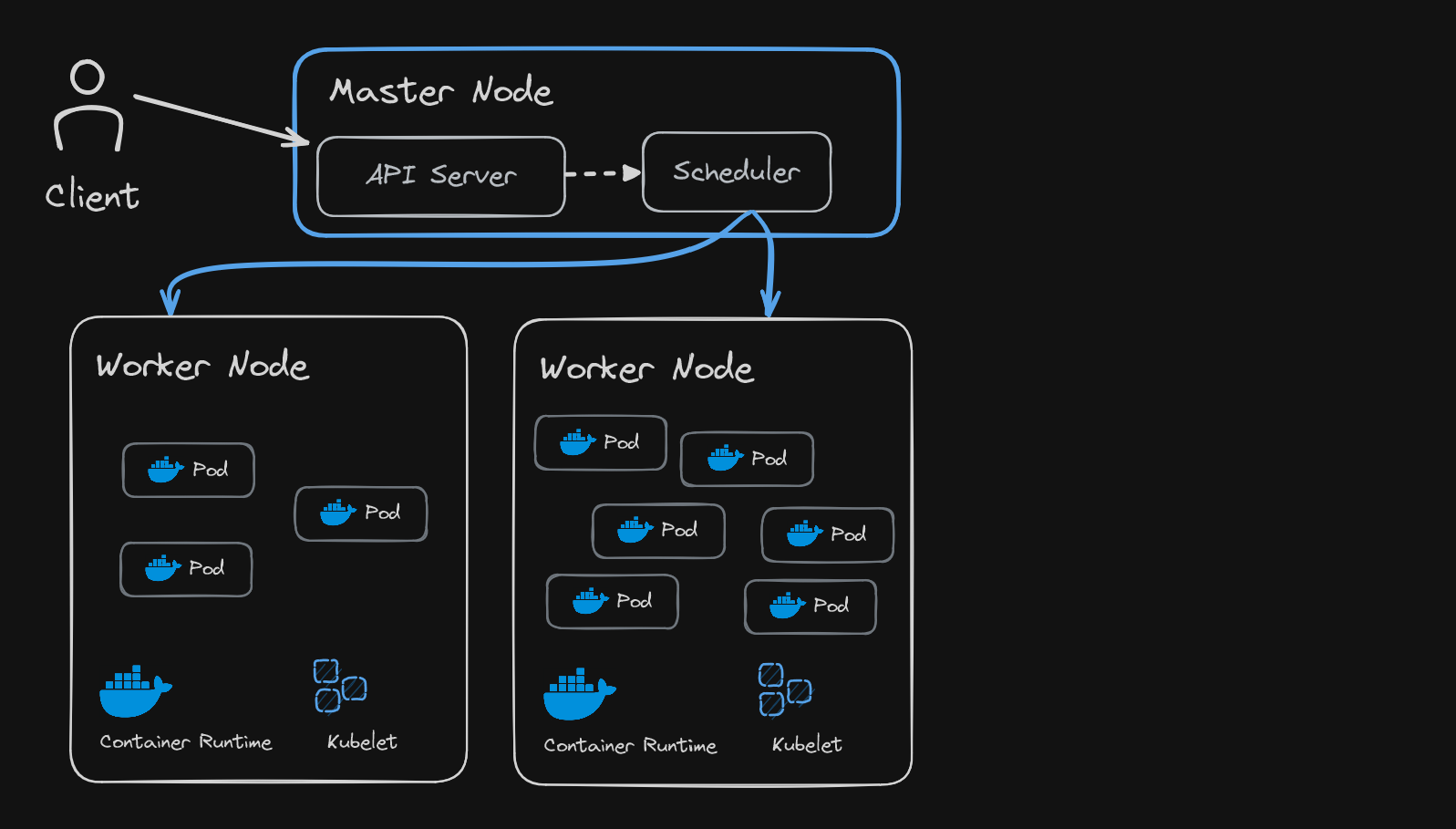
- Receives request -> Validates request -> Forwards to other processes
Scheduler
- After validation of request by the API server, request is received by Scheduler
- A request can be to start an application process in a worker node, so the schedular only decides on which node new pod should be scheduled
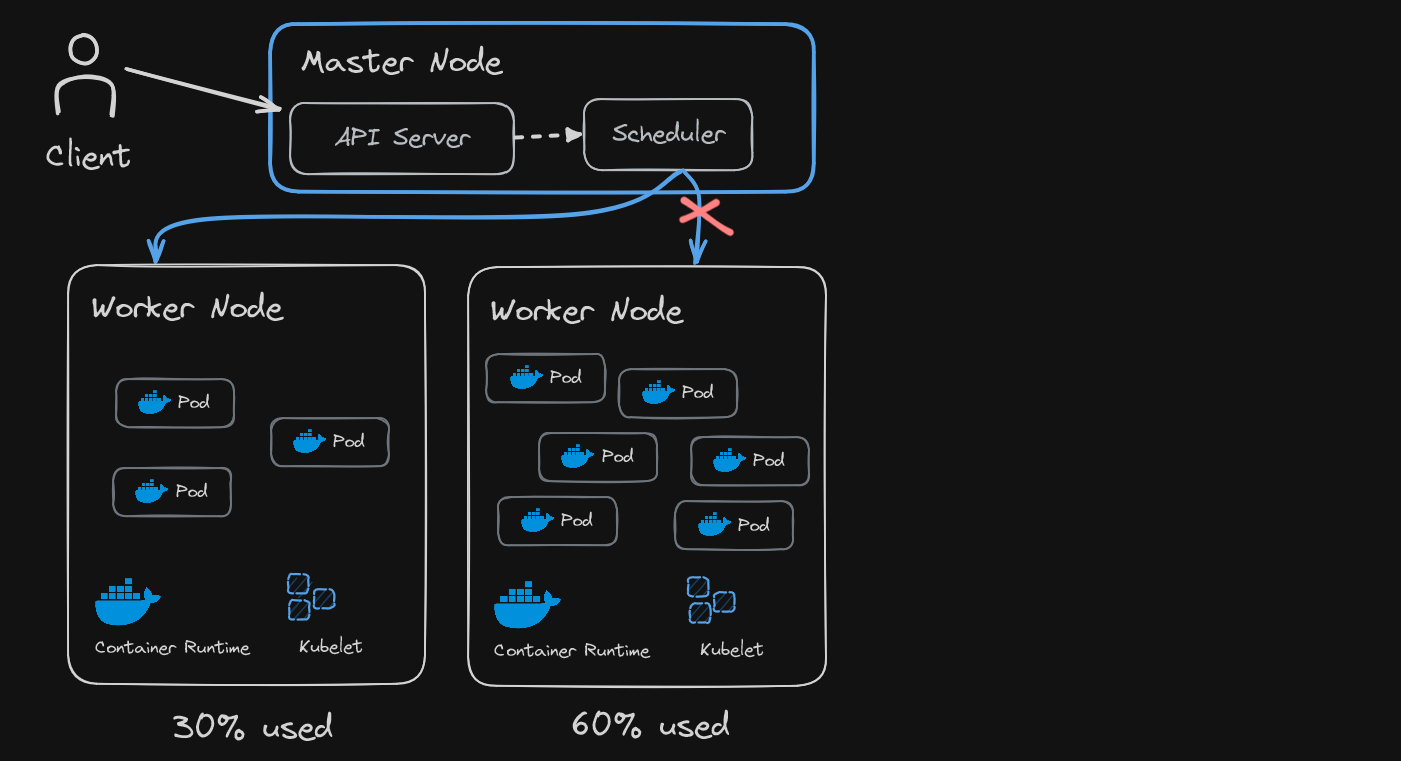
- Intelligently schedules pods to a node according to resources required, then request is forwarded to Kubelet for execution
Controller Manager
- When pods die, the controller manager detects state changes (like crashing of pods) and tries to recover the cluster state
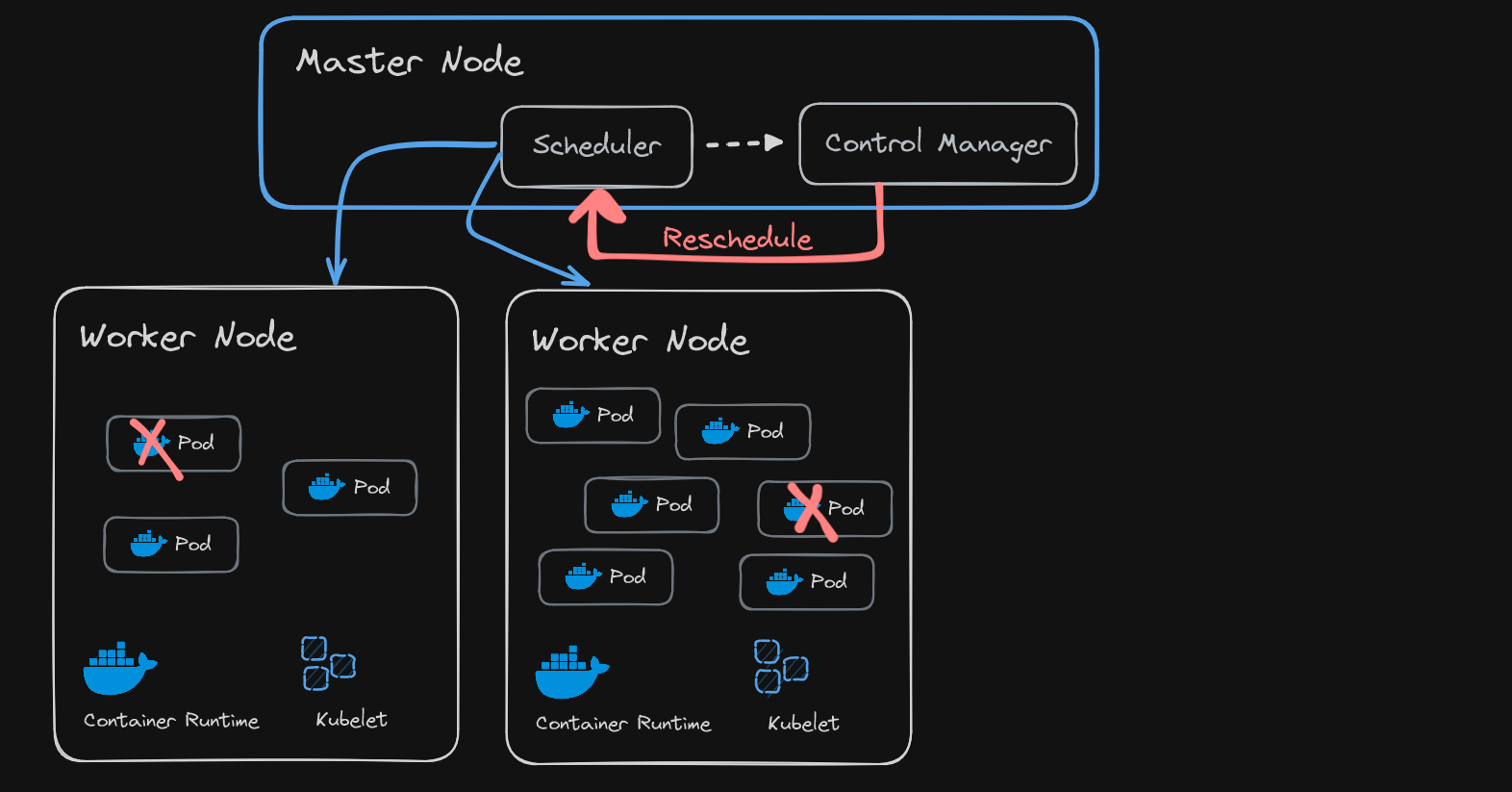
- So it requests the Scheduler to re-schedule the dead pods
Etcd
- Etcd is the cluster brain, which stores the cluster changes in a key value store, like
- cluster health
- resource availability
- cluster state changes
- No application data is not stored in etcd
Cluster
K8s Cluster may contain multiple master nodes and worker nodes.
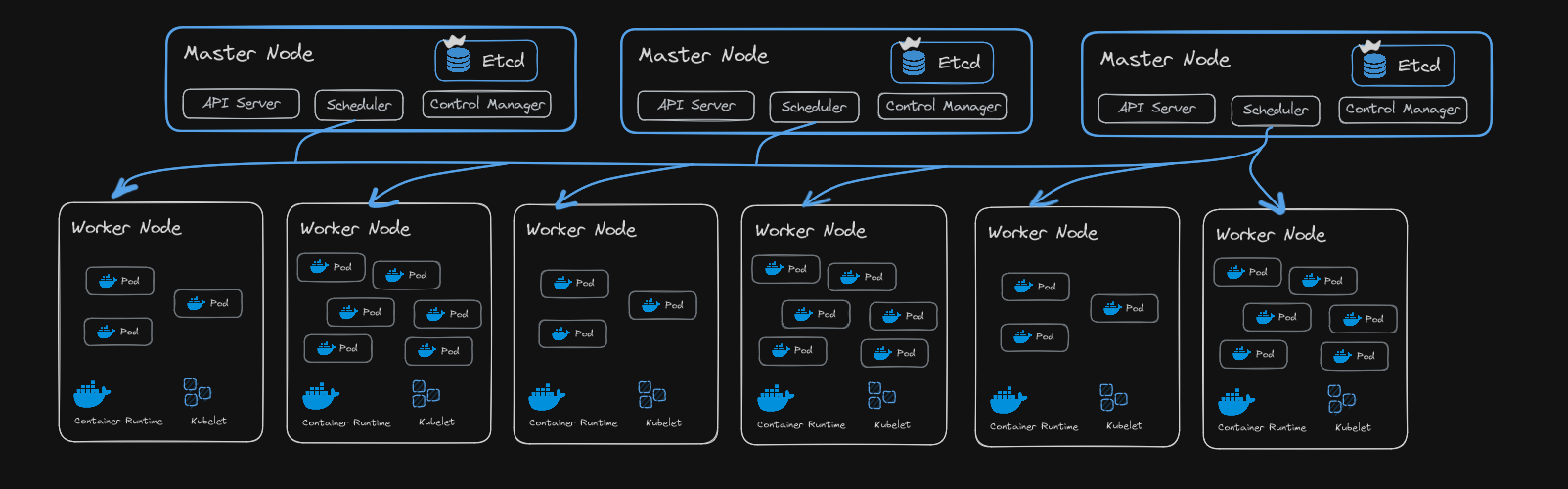
-
K8s Cluster = Control Plane + Nodes

-
Single Control Plane (Master Node):
-
It is a collection of various components which helps in managing the health of the overall cluster.
-
runs several processes that necessary to run and manage the cluster properly
-
API server is the front end for the Kubernetes control plane. (entry point of K8s cluster and is responsible for all communications) (listens to HTTPS port: 443 for requests)
- API: An application programming interface is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other.
-
Controller Manager (ensures proper working of the containers)
functions: desired state, current state, differences, making changes
- using "Kubectl" which is K8s CLI, it communicates with API server for execution (imperative way)
- using manifest files present in worker nodes like .yaml files (declarative way)
-
Scheduler (responsible for scheduling containers in nodes based on workloads, it listens to the API server)
-
ECTD key value storage (it holds current state of K8s cluster, configuration data of each node and takes snapshots for backup and restoration)
- Consistent and highly-available key value store used as Kubernetes' backing store for all cluster data
-
-
multiple Data Plane (Worker Nodes):
- 'Kubelet' process running, makes sure that containers are running in a Pod. (for communication with the API server and execute some tasks)
- 'Kube-Proxy' is responsible for networking and provides IP addresses to nodes.
- Worker Node -> Container Runtime -> Pod -> Container
- Pod is the smallest execution unit and containers in the same pod share their lifecycle and storage resources.
-
Virtual Network:
- it unifies all the nodes inside of a cluster into a power machine (which is a sum of all resources of all the individual worker nodes)
Master node need less resources than worker node.