Conditional Graph 🚧
Objectives ✅
- Implement conditional logic to route the flow of data to different nodes.
- Use Start and End nodes, to manage entry and exit points explicitly.
- Design multiple nodes to perform different operations(addition, subtraction).
- Create a router node to handel decision -making and control graph flow
from typing import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
class AgentState(TypedDict):
number1: int
operation: str
number2: int
finalNumber: intdef adder(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""This node adds two numbers together."""
state['finalNumber'] = state['number1'] + state['number2']
return state
def subtractor(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""This node subtracts two numbers."""
state["finalNumber"] = state["number1"] - state["number2"]
return state
def decide_next_node(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""This node will select the next node of the graph"""
if state["operation"] == "+":
return "addition_operation"
elif state["operation"] == "-":
return "subtraction_operation"
graph = StateGraph(AgentState)
graph.add_node("add_node", adder)
graph.add_node("subtract_node", subtractor)
graph.add_node("router", lambda state: state) # Pass-through Node
graph.add_edge(START, "router")
graph.add_conditional_edges(
"router",
decide_next_node,
{
# Edge: Node
"addition_operation": "add_node",
"subtraction_operation": "subtract_node"
}
)
graph.add_edge("add_node", END)
app = graph.compile()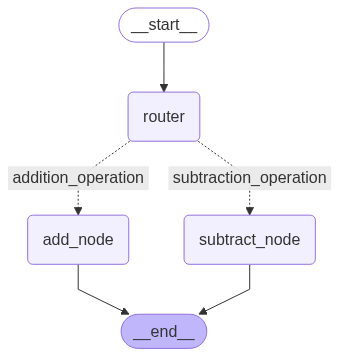
result = app.invoke({"number1": 15, "number2": 30, "operation": "+"})
print(result["finalNumber"])OUTPUT:
'45'