Looping Graph 🌌
Objectives ✅
- Implement looping logic to route the flow of data to different nodes.
- Create a single condition edge to handle decision-making and control graph flow.
from typing import TypedDict, List
import random
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
class AgentState(TypedDict):
name: str
number: List[int]
counter: intdef greeting_node(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""Greet the user and ask for their name."""
state['name'] = f"Hi, there, {state['name']}"
state["counter"] = 0
return state
def random_node(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""Generate a random number and add it to the list."""
state['number'].append(random.randint(1, 100))
state["counter"] += 1
return state
def should_continue(state: AgentState) -> AgentState:
"""Decide whether to continue looping based on the counter."""
if state["counter"] < 5:
print("ENTERING LOOP", state["counter"])
return "loop"
else:
print("EXITING LOOP", state["counter"])
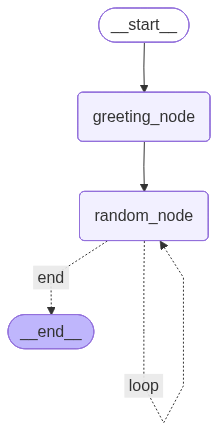
return "end"graph = StateGraph(AgentState)
graph.add_node("greeting_node", greeting_node)
graph.add_node("random_node", random_node)
graph.add_edge(START, "greeting_node")
graph.add_edge("greeting_node", "random_node")
graph.add_conditional_edges(
"random_node",
should_continue,
{
# Edge: Node
"loop": "random_node",
"end": END,
},
)
app = graph.compile()
app.invoke({"name": "Alice", "number": [], "counter": -1})OUTPUT:
ENTERING LOOP 1
ENTERING LOOP 2
ENTERING LOOP 3
ENTERING LOOP 4
EXITING LOOP 5
{'name': 'Hi, there, Alice', 'number': [97, 13, 7, 70, 58], 'counter': 5}