
Git Basics
- Version control is a system that records changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later.
- A Repository contains all of your project's files and each file's revision history.
3 States
Modified / Un-tracked
- changes are made in a file but have not been committed.
Staged
- a modified file is marked and is ready to get committed
Committed
- a snapshot of the data is permanently stored in git directory.
Creating new Git Repository
-
git initinitialises an empty git repository in the current directory. A “.git” file is created and hidden.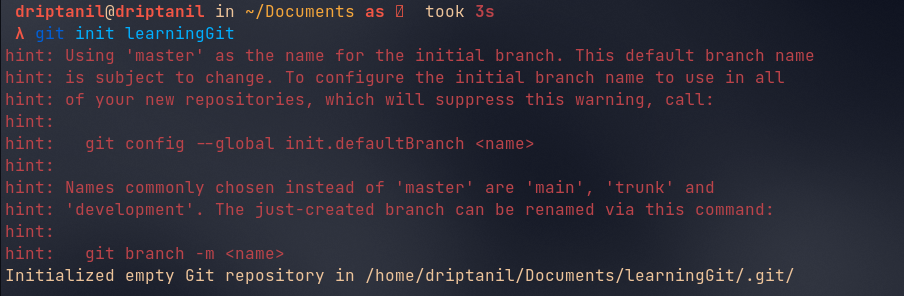
-
ls -ashows all the files including the hidden files.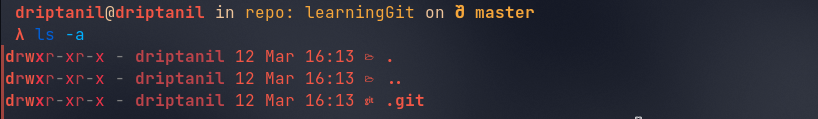
-
touch hello.txtwill create a file named “hello.txt”.
Git Status
git statusshows the status of the git repository.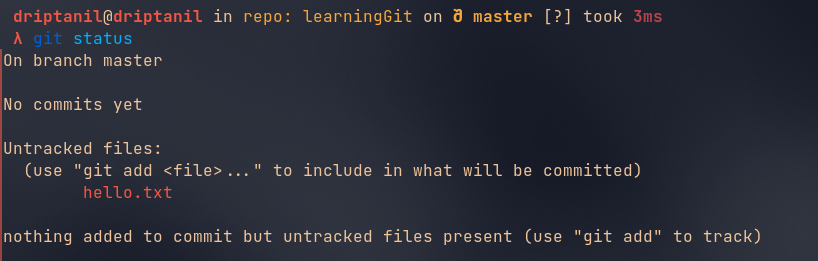
Git Add
git add <file>stages the changes of the file.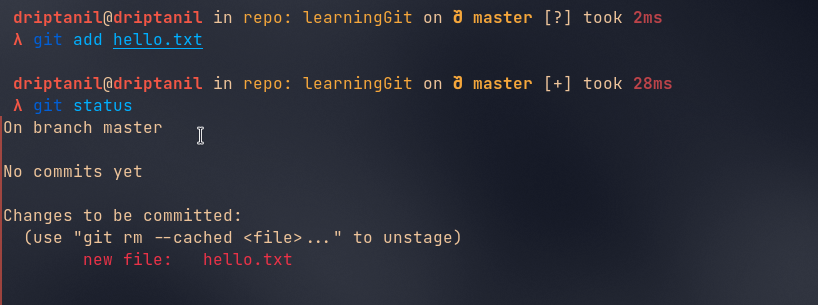
Git Commit
git commit -m "<commit_message>"commits to all the staged changes. “-m” adds name to the commit.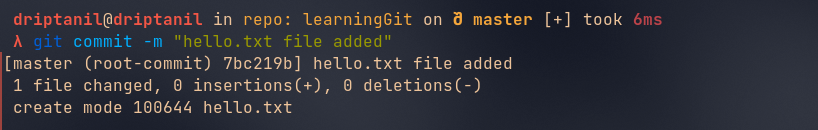
Git Log
git logwill show all the history of all commits.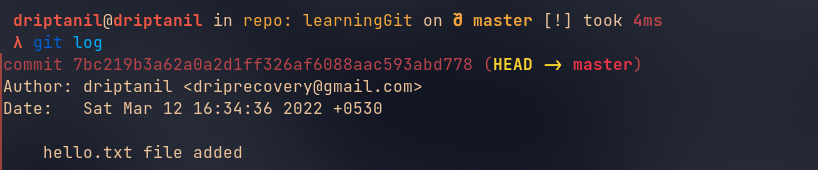
Git Restore
vim names.txtallows editing the file in the console, when files are modified after they are needed to be staged again.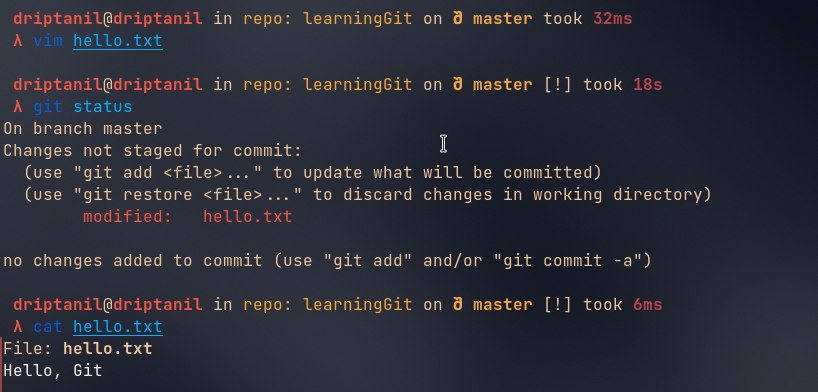
git restore --staged <staged_file>will remove staged changes for file from staged (only works after first commit).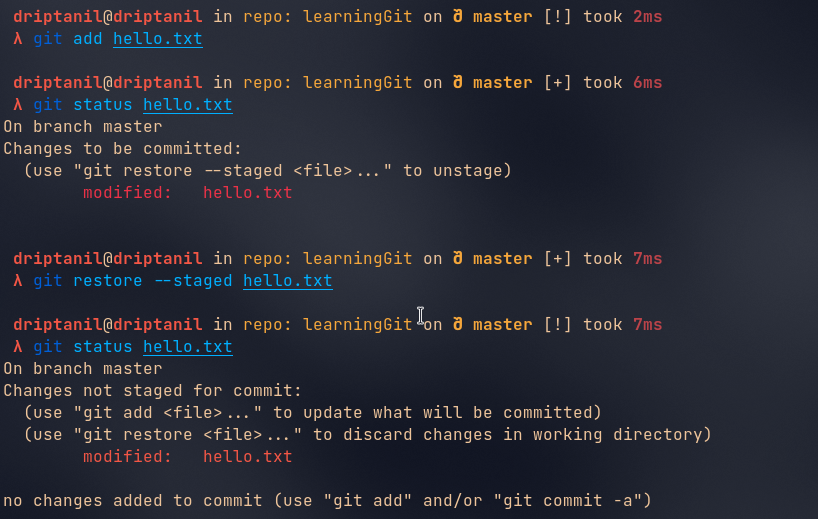
Git Reset
git reset <commit_id>will revert to the commit.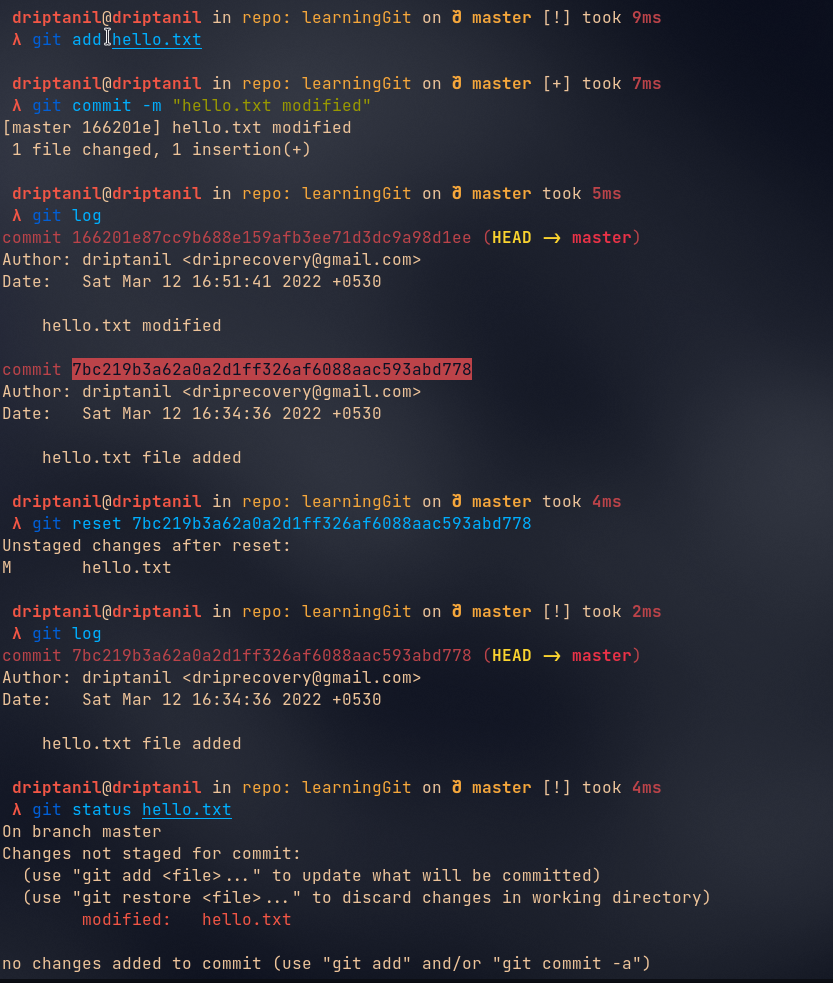
Git Stash
git stashwill neither commit the changes nor will delete all the changes, it just stores the changes somewhere else.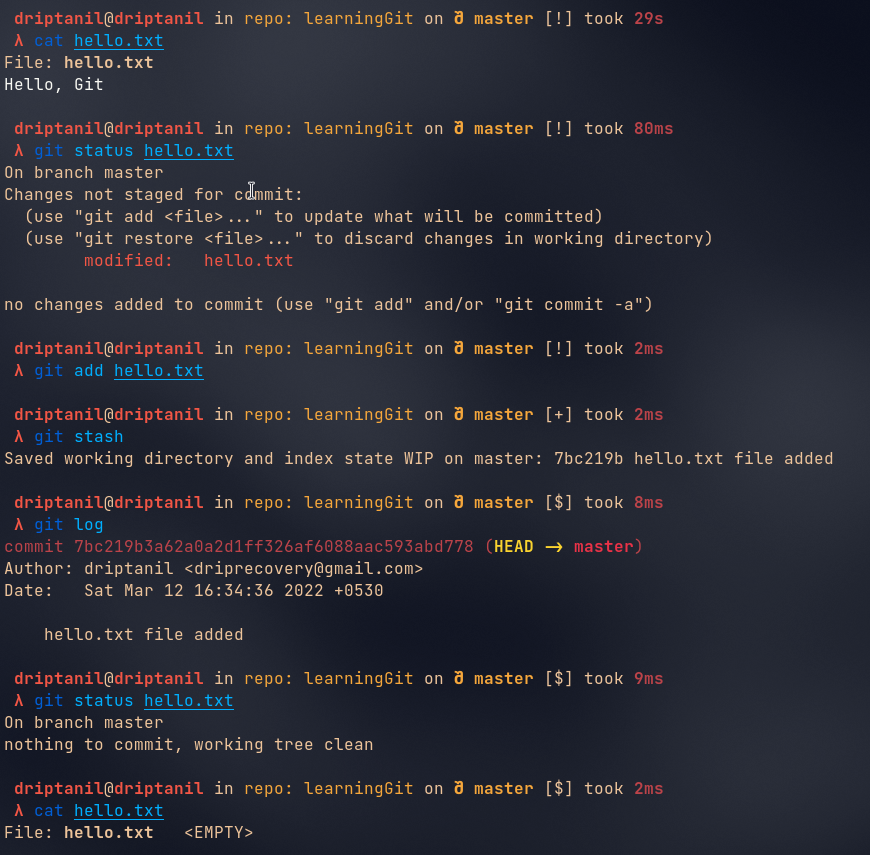
git stash popwill bring back all the changes stored somewhere else and will be staged.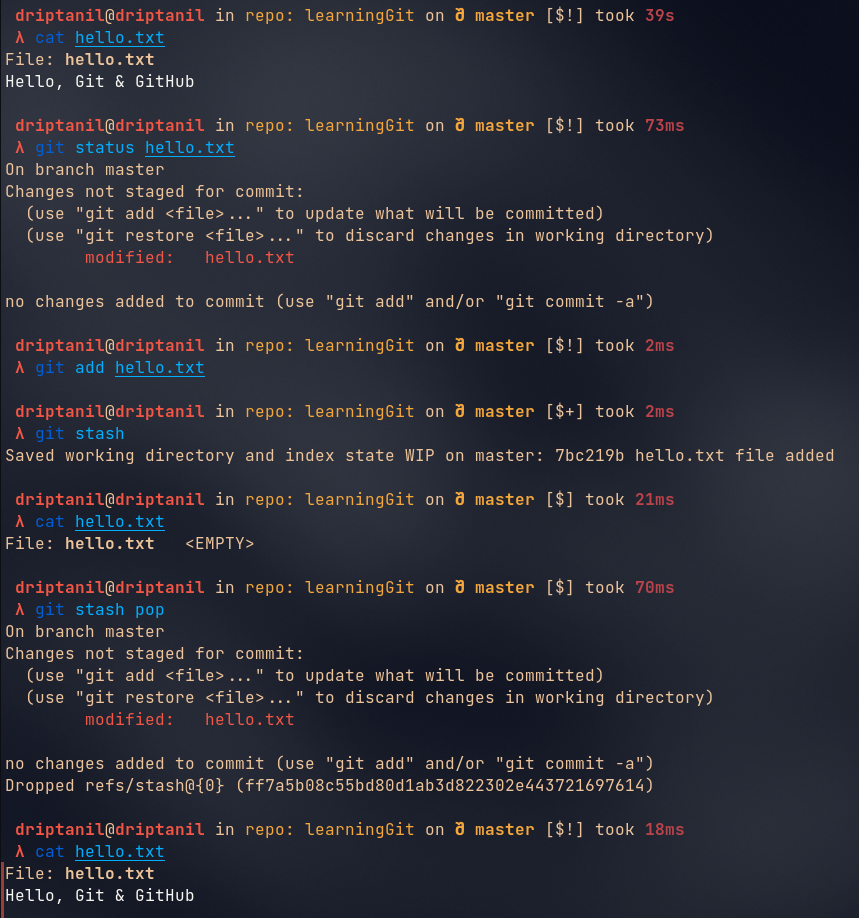
git stash clearwill remove all the changes that haven’t been staged or committed will be removed.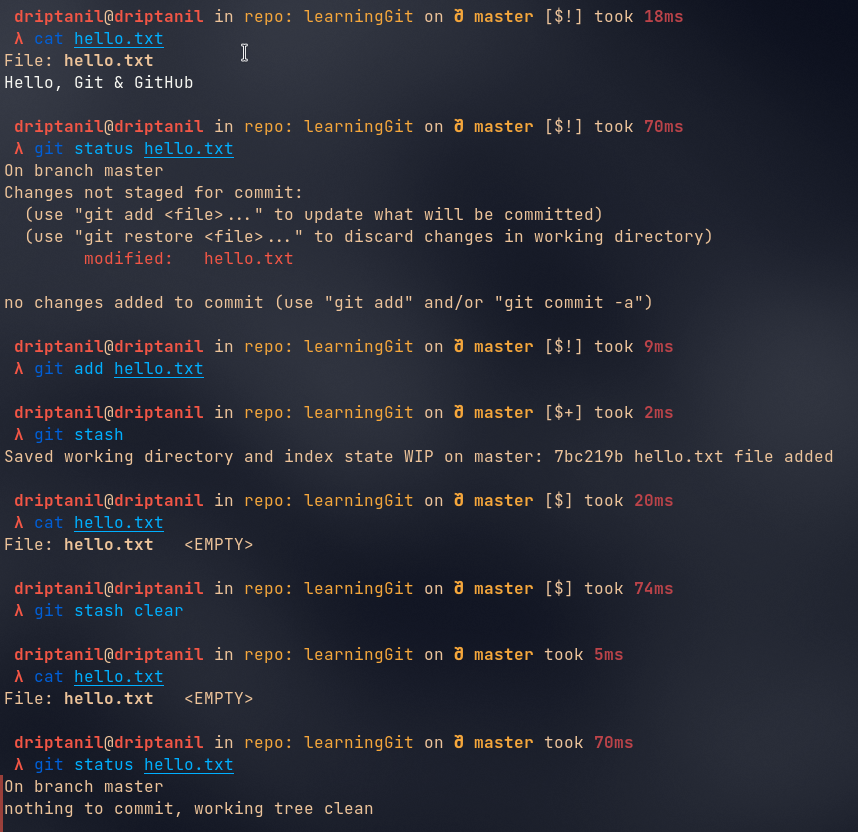
Adding Origin
git remote add origin https://github.com/<username>/<repository_link>will link the working directory to the GitHub repository.
Git Push
git push <repository-link>orgit push originwill push all the commits made in local git directory to remote repository. Does not work, now token are used for authentication of user. GitHub Personal Access Token Documentation (opens in a new tab)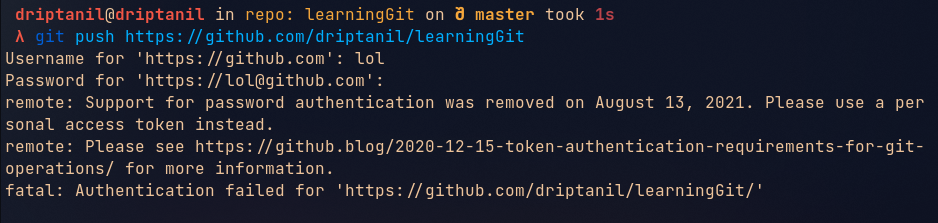
GitHub Personal Access Token (opens in a new tab):
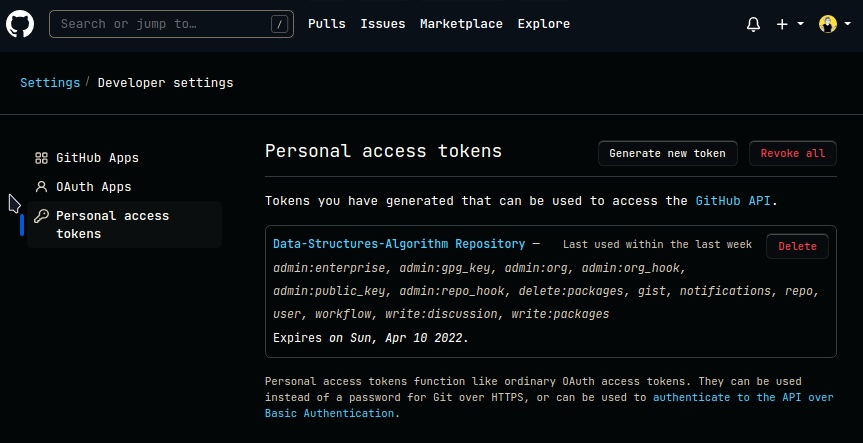
-
Click on
Generate new token -
Choose the permissions and validity of the token
-
Copy the token (Store it somewhere safe)
-
git push https://<token>@github.com/<username>/<repository_link>will push all the commits to the repository.
SSH Keys:
- Use
git clone git@github.com:<user>/<repository>.gitto clone repository.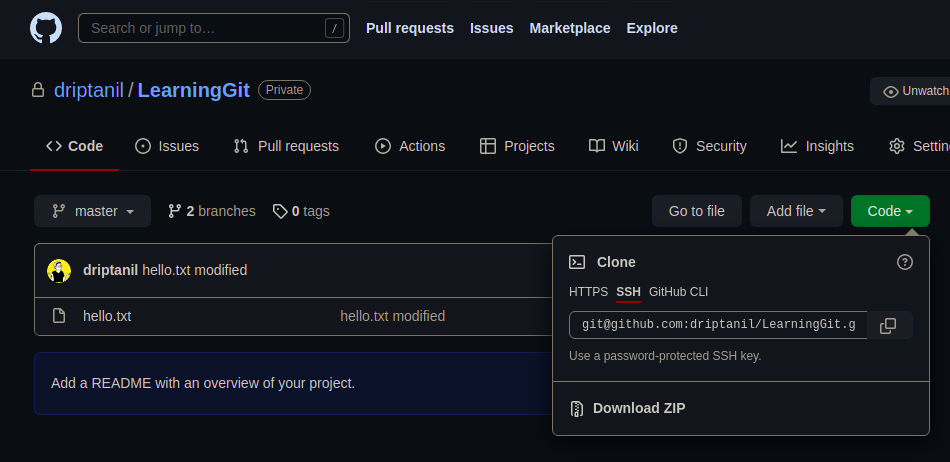
- Use
ssh-keygen -oto generate SSH key using git.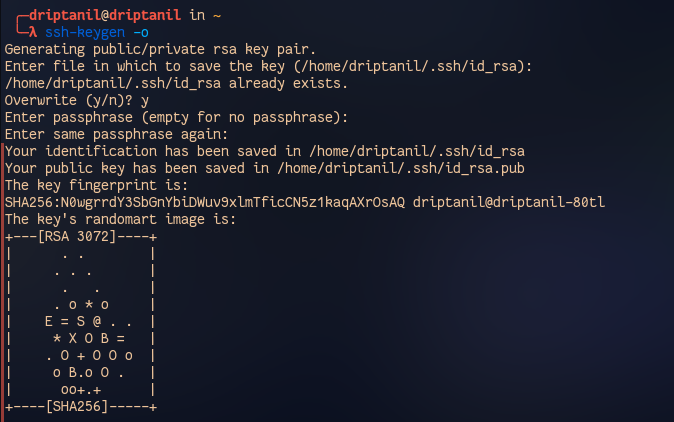
- Use
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub(this file contains the private SSH key) and select the contents and copy usingCtrl + Shift + C.
- Open
https://github.com/settings/keys(adding the private SSH key to GitHub), click onnew SSH keys. Paste the copied key in
Paste the copied key in keysection and add atitle.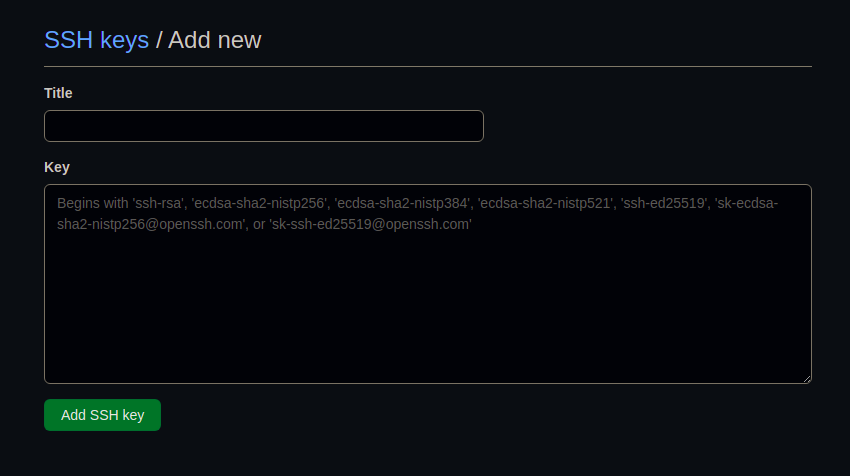
- Click on
Add SSH key.
Pulling Changes
git pull originwill pull all the commits made in the remote repository to the local git directory.
Cloning Repository
git clone <repository_link>will download all the files in the remote repository to a local git directory.
How to make contributions to the existing GitHub repository?
Forking a Repository
- No one except the owner of the GitHub repository is allowed to make changes directly to the repository.
Forkallows us to make a copy of the existing GitHub repository with our own ownership and in this repository, we are allowed to make changes directly.- The original repository which has been forked is known as the Upstream URL.