Git Branches
What is the use of Branches?
- When adding a feature or repairing a bug then always create a new branch.
- Never commit directly commit to the “main” or “master” branch which is the default branch of a GitHub Repository. Because in Open-Source Projects, code in “main” is used by everyone, and maybe our code may have some errors and is not finalised yet.
Head Branch
- It is the active and the checked out branch, commits are always made in Head Branch
- By default “HEAD” points to the “main” or “master” branch. Generally, commits are made on the “HEAD” inside the “.git” folder.
Local Branches
- The branches present in the local machine.
Remote Branches
- The branches present in remote location.
Creating new Branch
git branch <branch_name>creates a new local branch.
git branch <branch_name> <revision_id>creates a new local branch at the commit with revision_id
Switching Branches
-
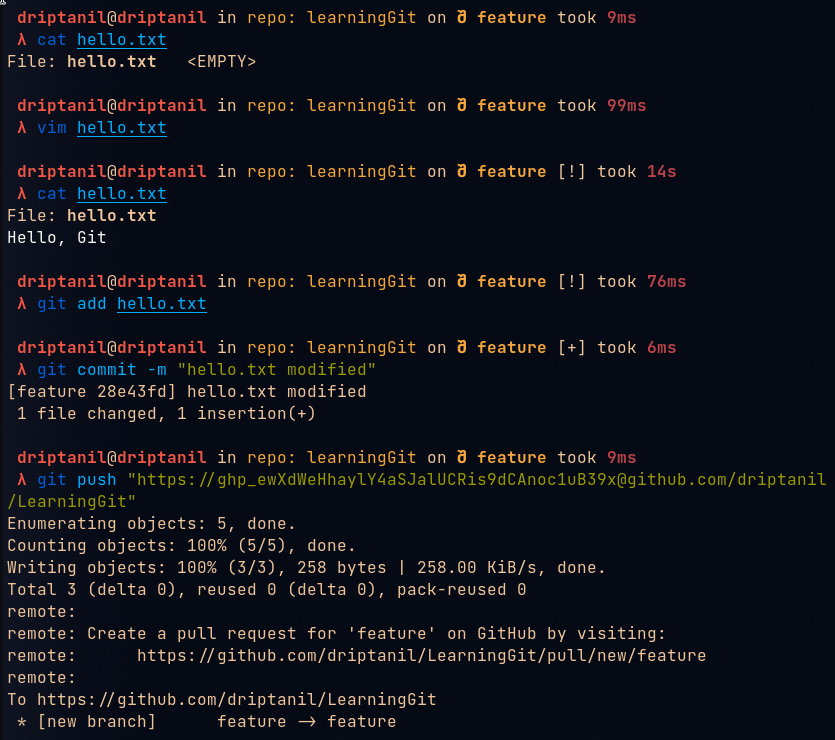
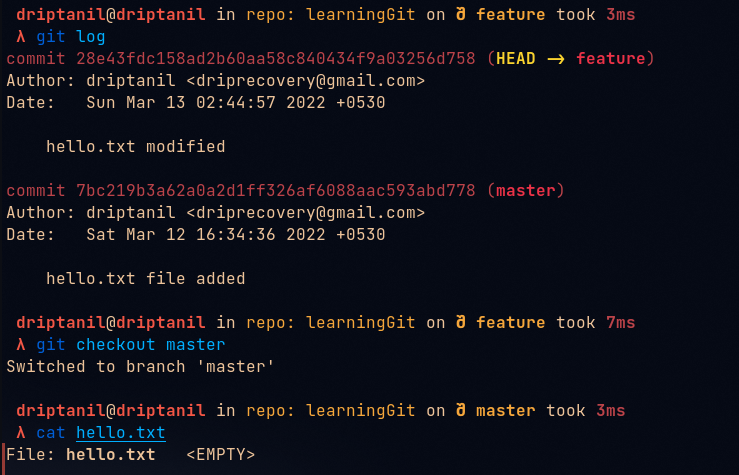
git checkout <branch>orgit switch <branch>is used to change “HEAD” which will now point to the branch.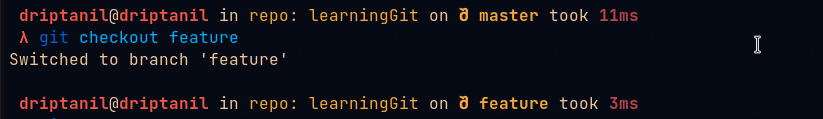
-
Now commits are made to the checked out branch and the “main” or “master” branch remains unchanged.
Renaming Branches
Local Branches
git branch -m <new_branch>will rename the current head branch.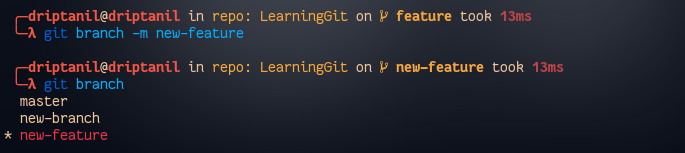
git branch -m <branch> <new_branch>will rename the branch.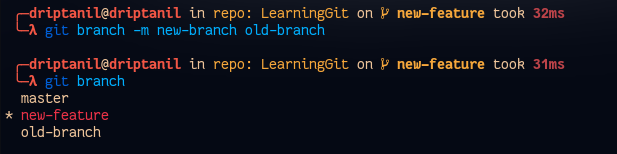
Remote Branches
Git Merge
git merge <branch>is used to update and merge all the changes made in the “feature” branch to the “main” or “master” branch.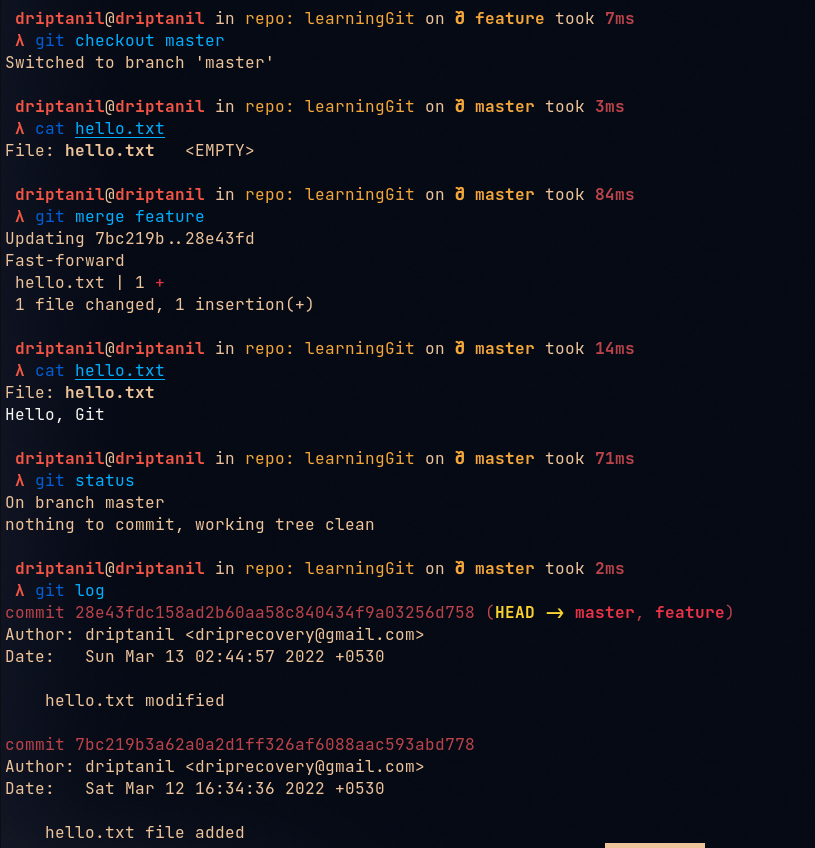
Publishing Branches
git push -u origin <branch>will push the local branch to remote. (-uhelps establish a tracking connection)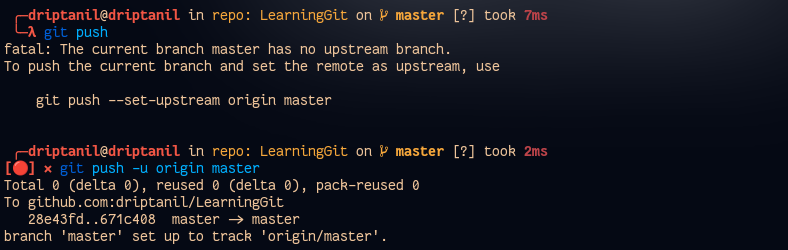
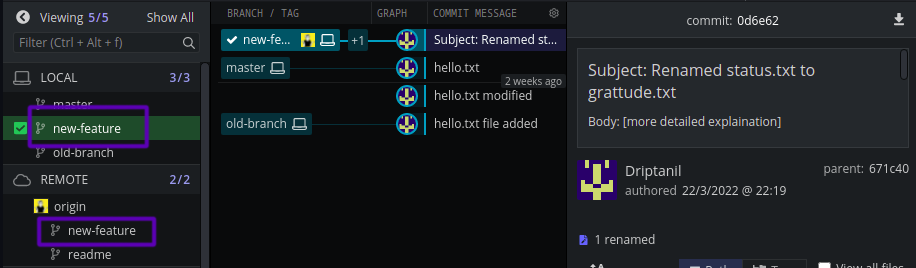
Tracking Connection
- By default, branches in git have no relation with each other.
git checkout --track <remote_branch>helps establish a tracking connection and adds the remote branch to locally.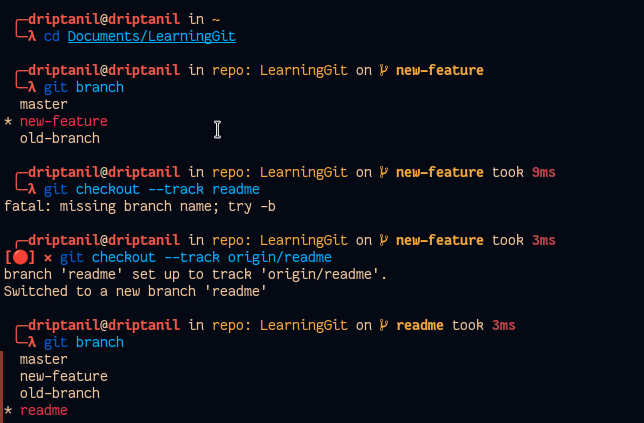
git branch --track <branch_name> <remote_branch>helps establish a tracking connection which allows branch to track remote branch.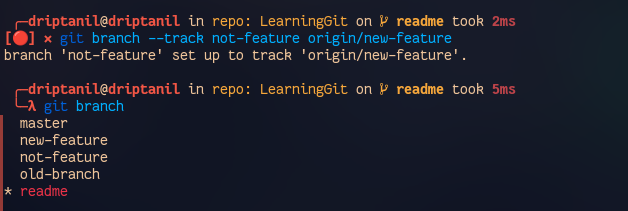
- It allows
git push&git pullin place ofgit push origin <branch>and also informs about unpulled and unpushed files usinggit branch -v.
Pulling Branch
git pullwill pull all the changes in remote branch to local branch.
Pushing Branch
git pushwill push all the changes in local branch to remote branch.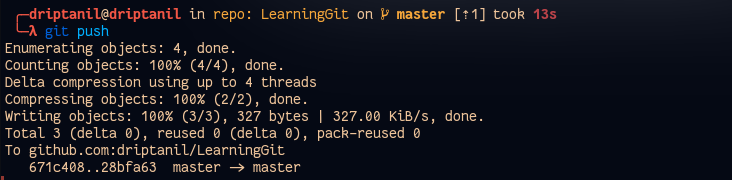
Deleting Branch
git branch -d <branch>will delete the branch, but it will not remove the branch which is currently head.

git branch -D <branch>will force delete the branch with not pushed files.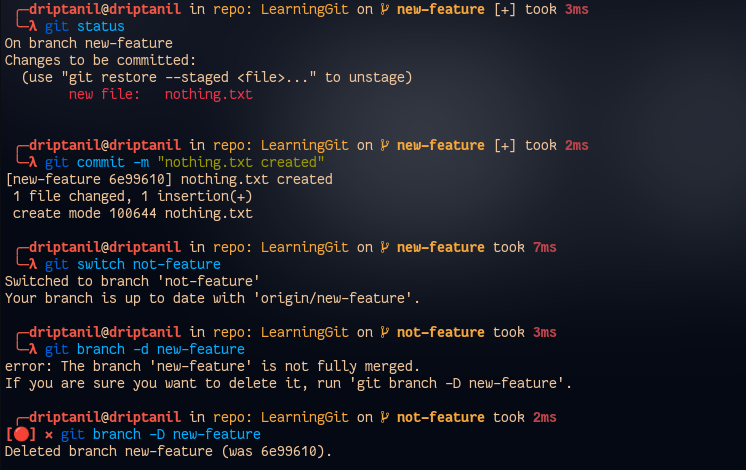
git push origin --delete <branch>will remove delete remote branches.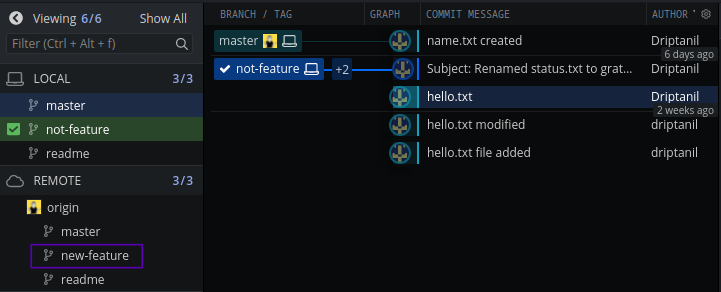
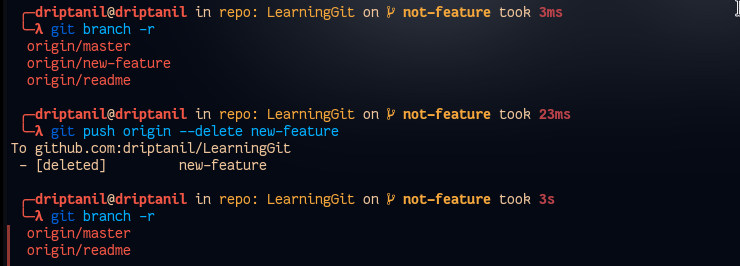
Merging Branch
git merge <branch>integrates the changes of the branch in the local head branch.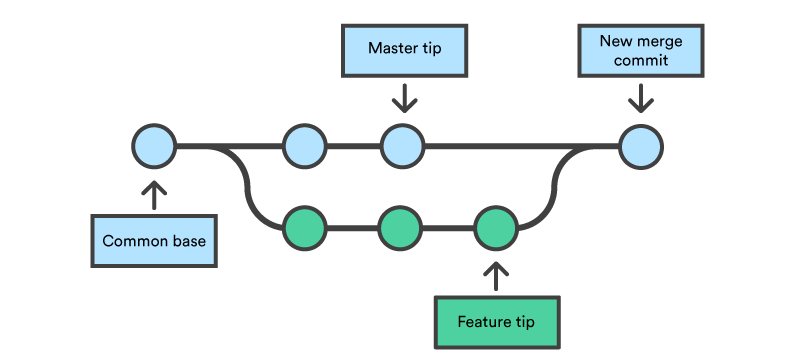
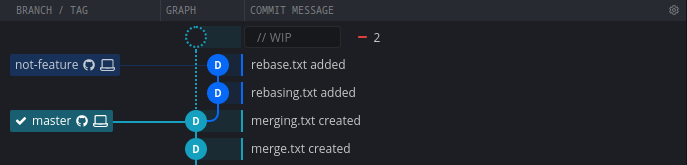
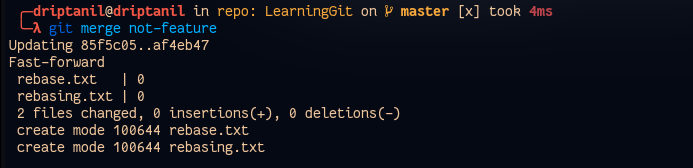
Rebasing Branch
git rebase <branch>integrates the changes of branch with the local head branch.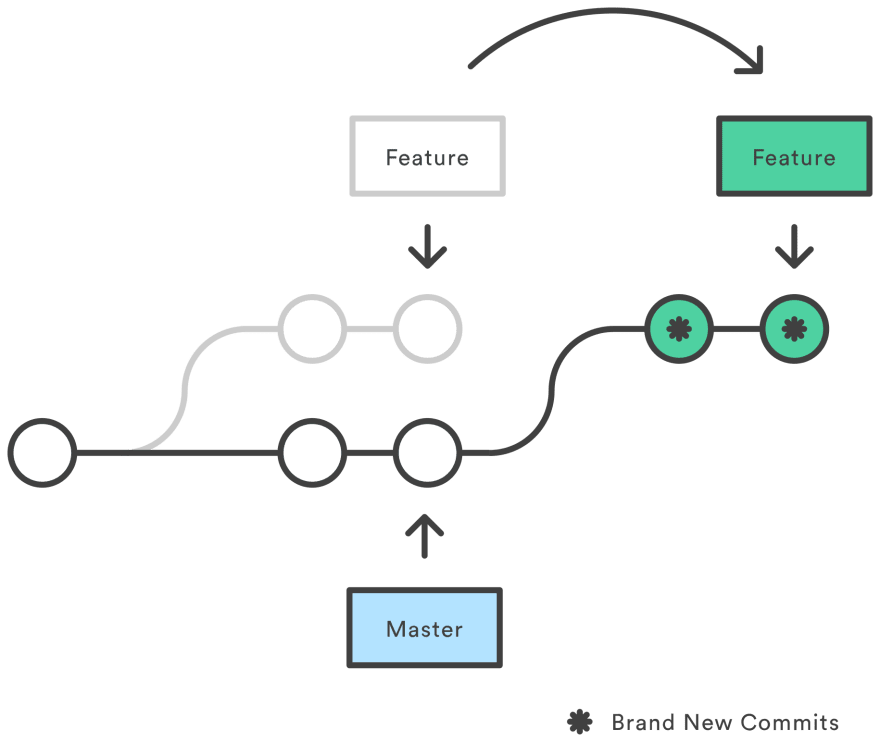

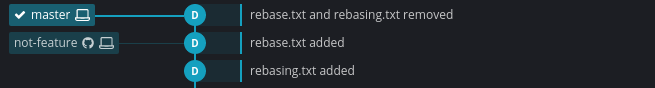
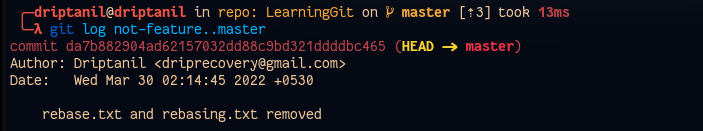
Comparing Branches
git log <branch>..<another_branch>displays the commits which are made in a branch but not in other branch.